Stored procedures are pieces of reusable code that you can save in a database data dictionary. They help you extract, edit, and remove data from a database without writing the code to do so again and again. It also saves your time, lessens your workload, and increases your productivity.
Follow these steps to use stored procedures in a Blazor application:
Create a new Blazor application and add the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore, Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer, Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design, Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools NuGet packages using the NuGet package manager.
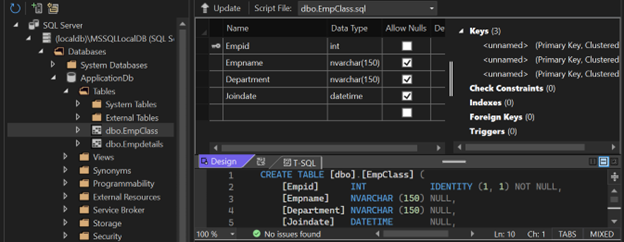
Create a class named EmpClass.cs in the Data folder and define the properties that are already in the database table.
[Empclass.cs]public class EmpClass
{
[Key]
public int Empid { get; set; }
public string? Empname { get; set; }
public string? Department { get; set; }
public DateTime joinDate { get; set;}
}
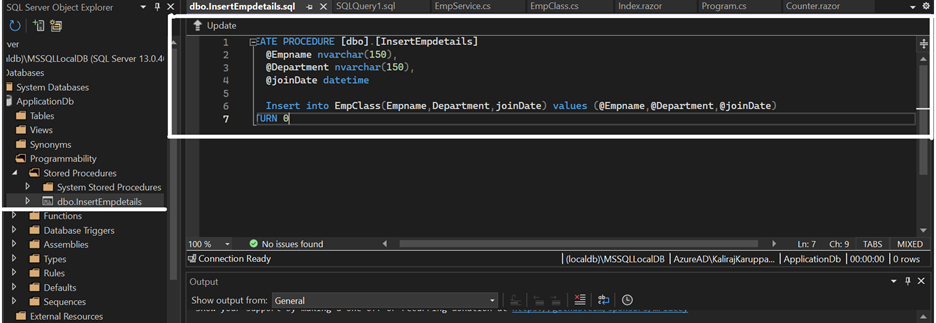
Also Define inserted Employee Details in stored procedure.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[InsertEmpdetails]
@Empname nvarchar(150),
@Department nvarchar(150),
@joinDate datetime
AS
Insert into EmpClass(Empname,Department,joinDate) values (@Empname,@Department,@Joindate)
RETURN 0Add the virtual property for the DbSet from EmpClass to insert records in the database under the Data folder.
[ApplicationDbContext.cs]public class ApplicationDbContext:DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptionsoptions ) : base(options)
{
}
public virtual DbSetInsertRecord { get; set; }
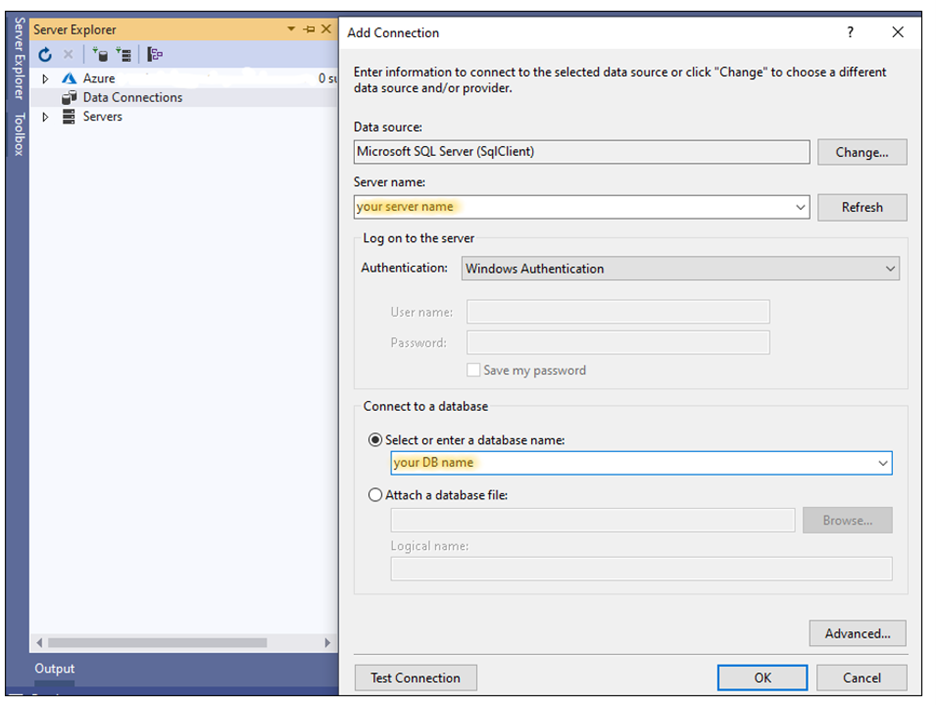
}Connect the SQL Server database to the Blazor application by choosing (View –> Server Explorer). Right-click the Data Connections and choose Add connection in Visual Studio. Add your server name and DB name to connect the database to the Blazor application.

The database is now connected to the Blazor application.Add the connection string configurations to the appsetting.json file.
[appsetting.json]{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Myconnection": " "Data Source={{Server_Name}};Initial Catalog={{DataBase_Name}};Integrated Security=True""
},
"Logging": {
……
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}Create an EmpServices class in the Services folder and define the ExecuteSqlRaw extension method to execute a stored procedure.
[EmpServices.cs]using {Your App Name}.Data;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace {Your App Name}.Services
{
public class EmpService
{
protected readonly ApplicationDbContext? _dbcontext;
public EmpService ( ApplicationDbContext? _db )
{
_dbcontext = _db;
}
public EmpClass AddNewRecord ( EmpClass? ec)
{
//Here define the ExecuteSqlRaw extension method to execute a stored procedure with InsertEmpdetails
_dbcontext!.Database.ExecuteSqlRaw("InsertEmpdetails {0},{1},{2}", ec?.Empname!, ec?.Department!, ec!.Joindate);
_dbcontext.SaveChanges();
return ec;
}
}
}Add the DbContext configuration to the Program.cs file.
builder.Services.AddDbContext(options => options.UseSqlServer("name=ConnectionStrings:Myconnection"));
builder.Services.AddScoped(); Insert Record Into Database Using Stored Procedure implement in index.razor page
@page "/"
@using {Your App Name}.Data
@using {Your App Name}.Services
@inherits OwningComponentBase<EmpService>
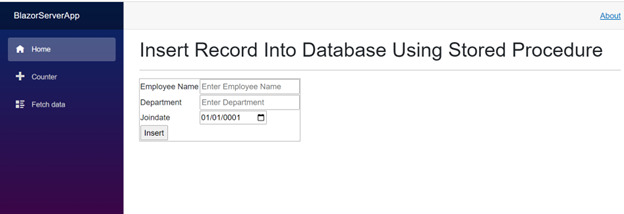
<h1>Insert Record Into Database Using Stored Procedure</h1>
<hr/>
<EditForm Model="@ec" OnValidSubmit="@Insertdata">
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>Employee Name</td>
<td><input type="text" placeholder="Enter Employee Name" @bind="ec.Empname"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Department</td>
<td><input type="text" placeholder="Enter Department" @bind="ec.Department" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Joindate</td>
<td><InputDate @bind-Value="ec.Joindate"></InputDate></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Joindate</td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Insert"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</EditForm>
@code{
EmpClass ec = new EmpClass();
void Insertdata ()
{
ec.Empid = 0;
Service.AddNewRecord(ec);
}
}Press Ctrl + F5 to run the application and see the output in the following image.





Share with