Instead of using the DataAnnotationValidator in Blazor, you can use FluentValidation to implement form validation. FluentValidation is a common validation library for.NET Core that offers a few advantages over the built-in DataAnnotations validation library, such as a larger set of rules, simpler setup, and extensibility.
To use fluent validation in a Blazor application:
Create a Blazor application using the link.
Install the “FluentValidation” package using the NuGet package manager.
Create a new folder named FluentValidation in the main application and add the following *.cs files – Employee, EmployeeValidator, FluentValidationValidator to it as shown below.

Add a model Employee class name in the Employee.cs file.
namespace {AppName}.FluentValidation
{
public class Employee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Organization { get; set; }
}
}- To write a model validator, you must create a EmployeeValidator class that is inherited from the AbstractValidator<Employee> and then add all the validation rules for the respective model to the constructor.
In FluentValidationValidator.cs, create a new validator component named FluentValidationValidator to replace DataAnnonationsValidator, and add the code below to it.
The FluentValidationValidator receives an EditContext as a cascading parameter and hooks into the EditContext’s OnFieldChanged and OnValidationRequested events to know when something is happening in the UI. It can add or remove validation messages from a ValidationMessageStore at any time.using System;
using FluentValidation;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Forms;
namespace {AppName}.FluentValidation
{
public class FluentValidationValidator<TValidator> : ComponentBase where TValidator : IValidator, new()
{
private readonly static char[] separators = new[] { '.', '[' };
private TValidator validator;
[CascadingParameter]
private EditContext EditContext { get; set; }
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
validator = new TValidator();
var messages = new ValidationMessageStore(EditContext);
/* Re-validate when any field changes or when the entire form requests validation.*/
EditContext.OnFieldChanged += (sender, eventArgs)
=> ValidateModel((EditContext)sender, messages);
EditContext.OnValidationRequested += (sender, eventArgs)
=> ValidateModel((EditContext)sender, messages);
}
private void ValidateModel(EditContext editContext, ValidationMessageStore messages)
{
var context = new ValidationContext<object>(editContext.Model);
var validationResult = validator.Validate(context);
messages.Clear();
foreach (var error in validationResult.Errors)
{
var fieldIdentifier = ToFieldIdentifier(editContext, error.PropertyName);
messages.Add(fieldIdentifier, error.ErrorMessage);
}
editContext.NotifyValidationStateChanged();
}
private static FieldIdentifier ToFieldIdentifier(EditContext editContext, string propertyPath)
{
var obj = editContext.Model;
while (true)
{
var nextTokenEnd = propertyPath.IndexOfAny(separators);
if (nextTokenEnd < 0)
{
return new FieldIdentifier(obj, propertyPath);
}
var nextToken = propertyPath.Substring(0, nextTokenEnd);
propertyPath = propertyPath.Substring(nextTokenEnd + 1);
object newObj;
if (nextToken.EndsWith("]"))
{
nextToken = nextToken.Substring(0, nextToken.Length - 1);
var prop = obj.GetType().GetProperty("Item");
var indexerType = prop.GetIndexParameters()[0].ParameterType;
var indexerValue = Convert.ChangeType(nextToken, indexerType);
newObj = prop.GetValue(obj, new object[] { indexerValue });
}
else
{
var prop = obj.GetType().GetProperty(nextToken);
if (prop == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException($"Could not find property named {nextToken} in object of type {obj.GetType().FullName}.");
}
newObj = prop.GetValue(obj);
}
if (newObj == null)
{
return new FieldIdentifier(obj, nextToken);
}
obj = newObj;
}
}
}
}Add the following code to the Index.razor page to perform fluent validation using the FluentValidationValidator component and its model validator (EmployeeValidator) in the EditForm component.
@page "/"
@using {AppName}.FluentValidation;
<EditForm Model="employee" OnValidSubmit="SubmitForm">
<FluentValidationValidator TValidator="EmployeeValidator" />
<ValidationSummary />
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="employee.Name" class="form-control" id="name" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="age">Organization:</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="employee.Organization" class="form-control" />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</EditForm>
@code {
Employee employee { get; set; } = new Employee();
public void SubmitForm()
{
}
}

View Sample in GitHub
using FluentValidation;
namespace {AppName}.FluentValidation
{
public class EmployeeValidator : AbstractValidator<Employee>
{
public EmployeeValidator()
{
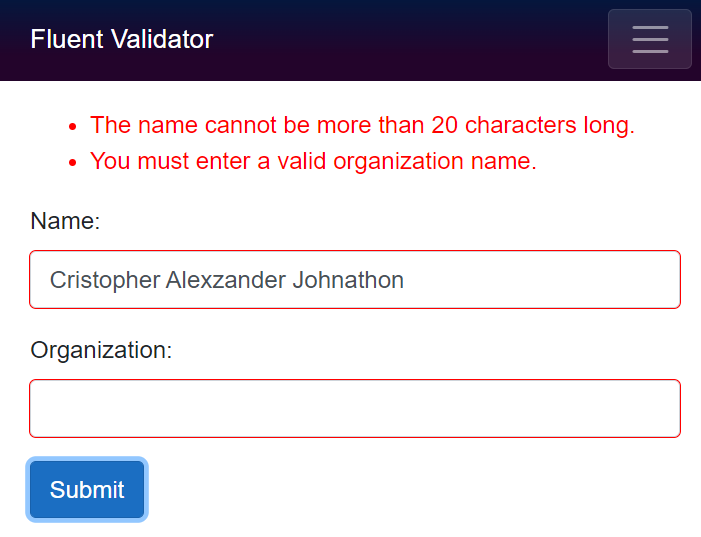
RuleFor(p => p.Name).NotEmpty().WithMessage("You must enter a valid name.");
RuleFor(p => p.Name).MaximumLength(20).WithMessage("The name cannot be more than 20 characters long.");
RuleFor(p => p.Organization).NotEmpty().WithMessage("You must enter a valid organization name.");
}
}
} 



Share with