
The Xamarin.Android Maps control is a powerful data visualization component that displays statistical information for a geographical area. It has highly interactive and customizable features such as zooming, panning, selecting, legends, markers, bubbles, and color mapping. Using the Maps control, you can render various maps, such as for sales, political boundaries, weather, elections, and route maps.

Shape layers provide options to render geographical shapes or custom shapes on maps.

Shapefiles (.shp) and GeoJSON (.json) data can be bound to maps to render any geometric shape.
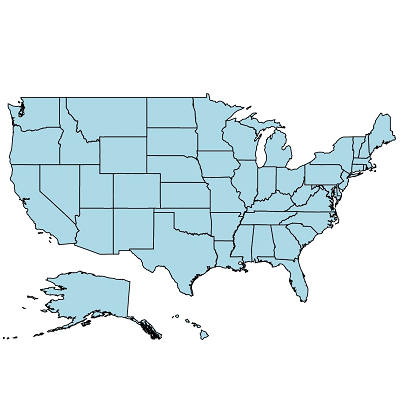
The default style of a shape can be customized using the color, stroke, and thickness properties.

The Xamarin.Android Maps control allows you to render any custom shape to make a map look like building infrastructure, a sports stadium, plane or bus seat arrangements, and more.

Load multiple shape files in a single map view. For example, add a sublayer over a main shape layer to view geographic features of a country such as rivers, valleys, and cities.
Imagery layers provide options to visualize satellite, aerial, and street maps, or other imagery tiles without using shapefiles.
Xamarin.Android OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a map of the world built by a community of mappers that is free to use under an open license. It allows users to view geographical data in a collaborative way from anywhere on Earth.
Xamarin.Android Bing Maps is a map of the entire world owned by Microsoft. It supports three types of map views: aerial, aerial with label, and road.
Set the initial zoom level automatically based on map Geo-bounds or distance (KM/miles) from the geo-point center value.
Map shapes can be easily annotated with labels to improve the readability of particular shapes’ names.

The look and feel of the default labels can be customized using the font style, size, and color properties.
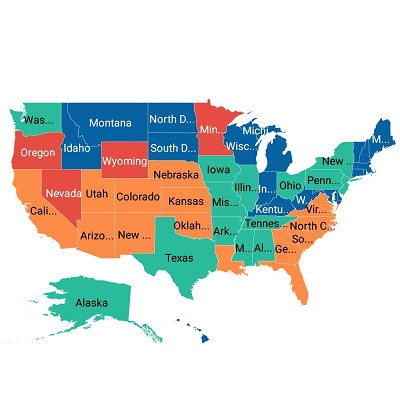
Labels can be aligned smartly within shape boundaries and can be trimmed or hidden to avoid labels overlapping.
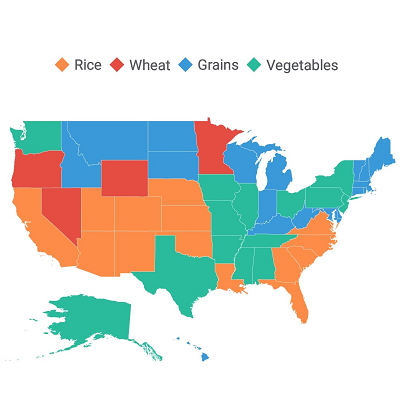
Produce a heat map by customizing the shape colors based on the underlying shape values.
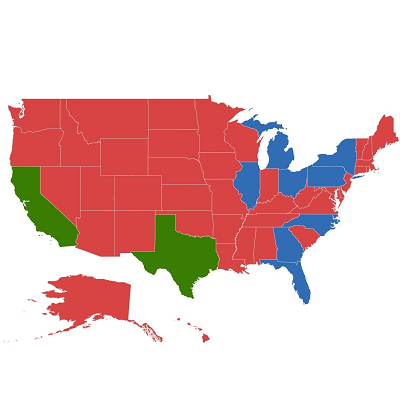
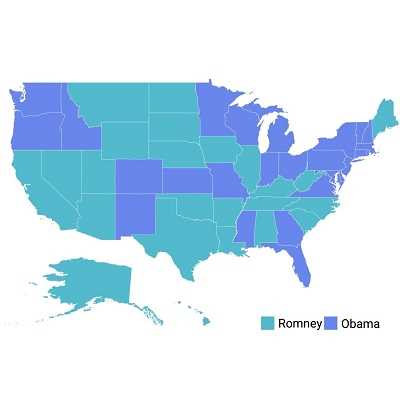
Equal color mapping differentiates a shape’s fill color based on its underlying value and color. For example, colors can be applied to states based on their winning political candidates.

Colors can be applied to shapes by comparing their values with desired numeric ranges. For example, colors can be applied to states based on their population density.
Markers allow you to denote a place with symbols or display some message at a specific latitude and longitude on a map.
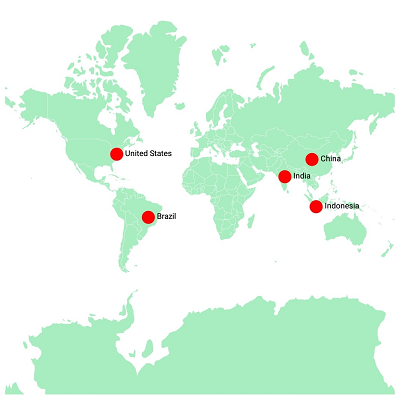
The marker type can be changed to built-in shapes such as circles, diamonds, rectangles, or squares to highlight a place.
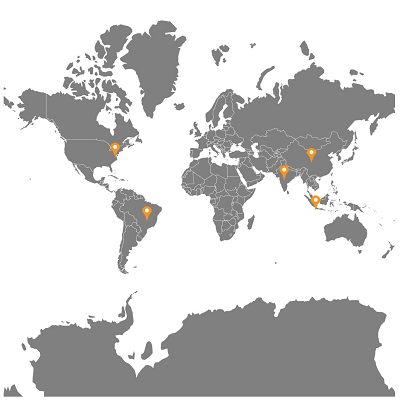
Markers can be customized by adding images or any custom shape to highlight a location.
Bubbles are used to add additional information to shapes such as population density or land area. They are rendered with various magnitudes and colors based on the underlying data values of the shapes.
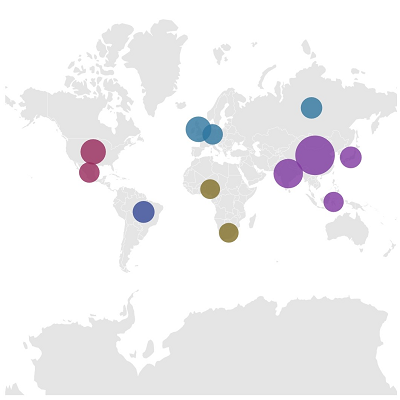
The default color of a bubble and its transparency can be customized using the fill and opacity properties.
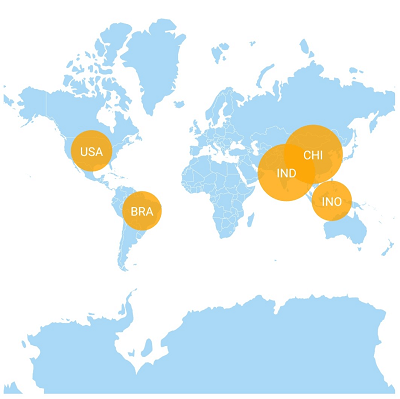
The minimum and maximum sizes of a bubble can be customized.
A legend is used to provide valuable information for interpreting maps with various colors, shapes, or other identifiers based on the data and application requirements.
The position of a legend can be changed or moved to any place inside a map.
The default size of a legend icon can be customized.
The end user experience is greatly enhanced by a set of user interaction features such as selection, zooming, and panning.
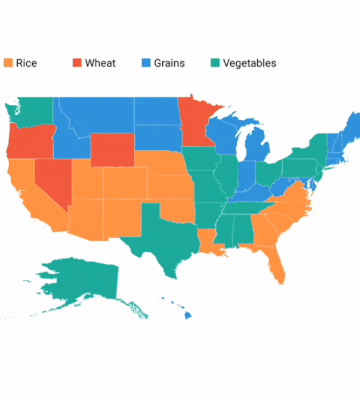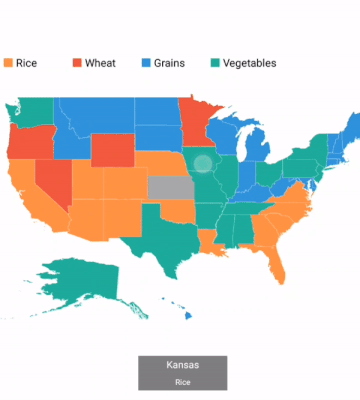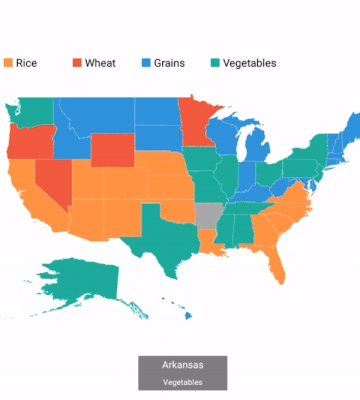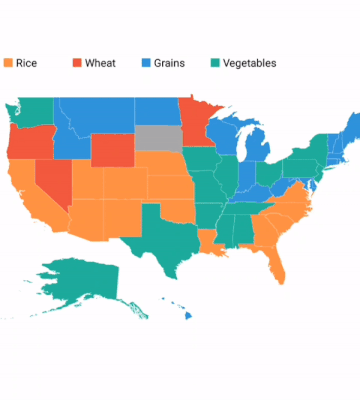
A particular area or shape can be selected or highlighted on user interaction to bring the center of the view over other shapes in a map.
Zooming allows end users to get a closer look at a particular area of interest on a map by stretching and pinching it.
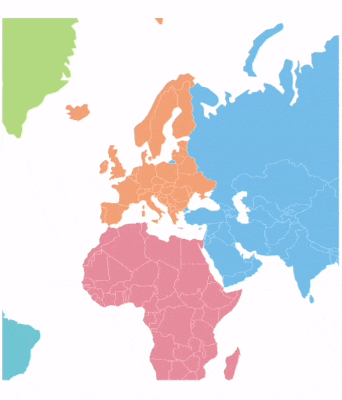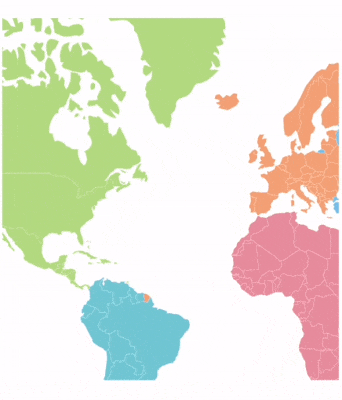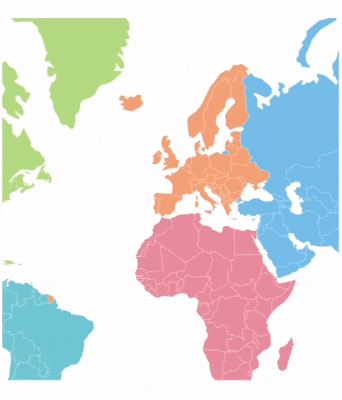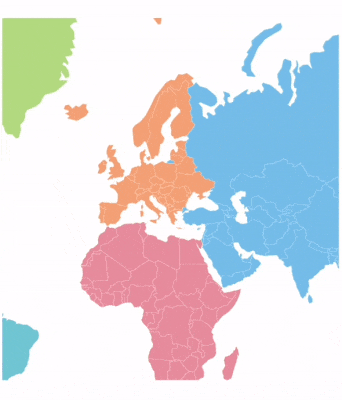
Panning allows end users to move a map around to focus on a specific area and navigate across its regions.
 Documentation
Documentation
Greatness—it’s one thing to say you have it, but it means more when others recognize it. Syncfusion® is proud to hold the following industry awards.