If you’re working in .NET MAUI, and you have two or more controls on top of each other that need to be revealed based on certain conditions, this article will undoubtedly assist you in handling that problem.
The order in which an element appears on the z-axis is represented by ZIndex, a property added in .NET MAUI Preview 12 to all the elements inherited from the IView interface. A control with a higher ZIndex value will be placed above others. For instance, a control with ZIndex 0 will be on the bottom, and control with ZIndex 1 or higher will be on the top (displayed).
In this blog, we’ll explore the ZIndex behaviors with default rendering and the procedure to bring .NET MAUI views to the front.
Rendering controls without handling ZIndex
The following code example defines view elements with a grid without defining ZIndex.
<Grid>
<Label Text="View 1" Margin="10,0,0,0" BackgroundColor="Green" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}" />
<Label Text="View 2" Margin="30,30,0,0" BackgroundColor="Navy" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
<Label Text="View 3" Margin="60,60,0,0" BackgroundColor="Yellow" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
<Label Text="View 4" Margin="90,90,0,0" BackgroundColor="SkyBlue" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
</Grid>
The following screenshot shows the result of the above XAML code.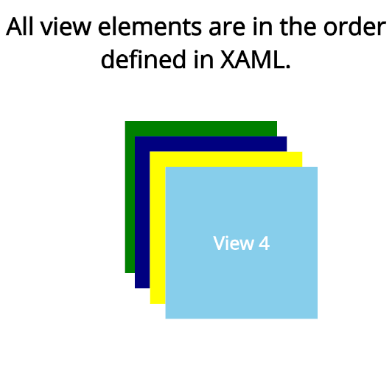
Rendering controls with ZIndex
In the following code example, each view is defined with a ZIndex value. Here, the last view which was painted as the top layer in the previous example is set with a lower ZIndex value compared to the other views.
<Grid>
<Label Text="View 1" ZIndex="4" Margin="10,0,0,0" BackgroundColor="Green" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}" />
<Label Text="View 2" ZIndex="3" Margin="30,30,0,0" BackgroundColor="Navy" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
<Label Text="View 3" ZIndex="2" Margin="60,60,0,0" BackgroundColor="Yellow" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
<Label Text="View 4" ZIndex="1" Margin="90,90,0,0" BackgroundColor="SkyBlue" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}"/>
</Grid>
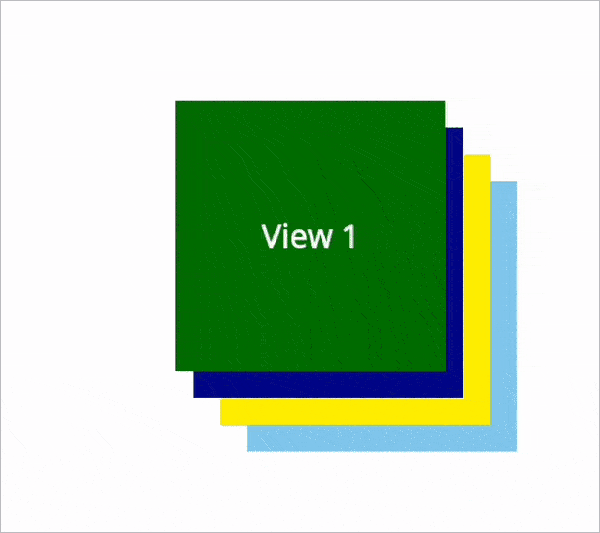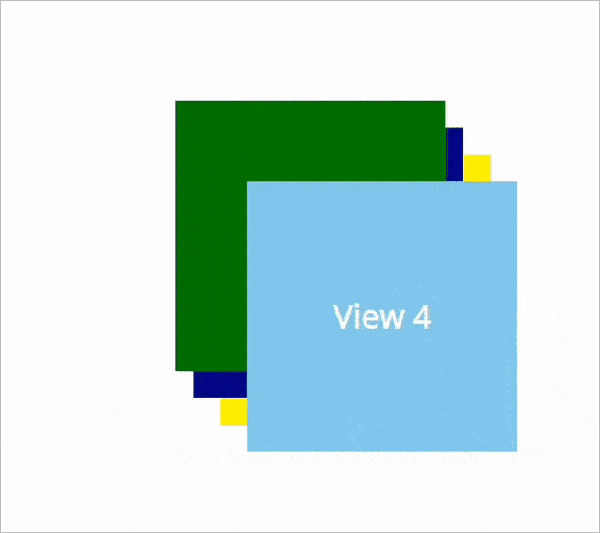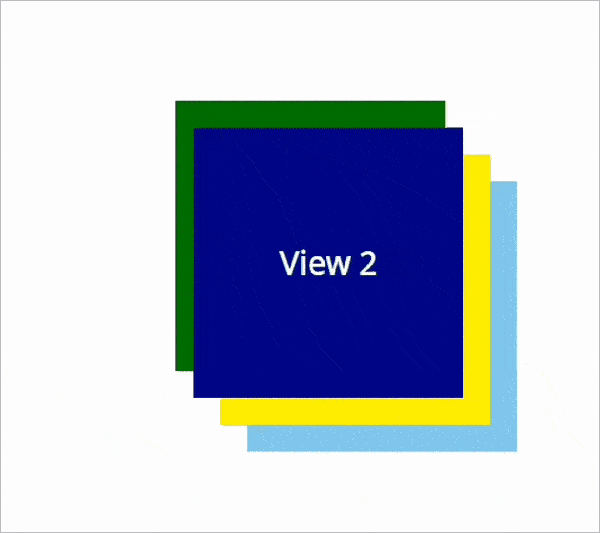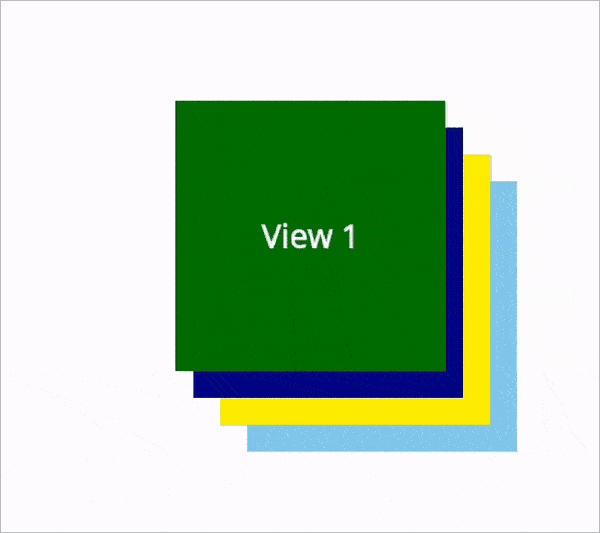
The views are rendered based on the assigned ZIndex values. Here, View1 is painted on top of the other layers as it has a higher ZIndex value.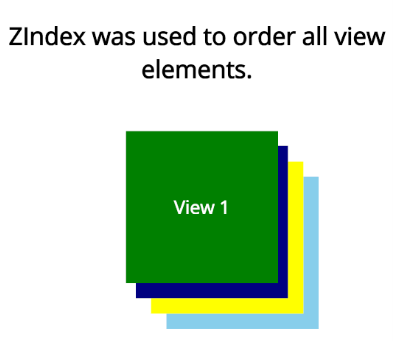
Bring the .NET MAUI views to the front
In the following code example, each view is defined with a ZIndex value during initial load.
<Grid>
<Label x:Name="view1" Text="View 1" ZIndex="4" Margin="10,0,0,0" BackgroundColor="Green" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}" >
<Label.GestureRecognizers>
<TapGestureRecognizer Command="{Binding BringToFront}" CommandParameter="{Binding Source={x:Reference view1}}"/>
</Label.GestureRecognizers>
</Label>
<Label x:Name="view2" Text="View 2" ZIndex="3" Margin="30,30,0,0" BackgroundColor="Navy" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}">
<Label.GestureRecognizers>
<TapGestureRecognizer Command="{Binding BringToFront}" CommandParameter="{Binding Source={x:Reference view2}}"/>
</Label.GestureRecognizers>
</Label>
<Label x:Name="view3" Text="View 3" ZIndex="2" Margin="60,60,0,0" BackgroundColor="Yellow" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}">
<Label.GestureRecognizers>
<TapGestureRecognizer Command="{Binding BringToFront}" CommandParameter="{Binding Source={x:Reference view3}}"/>
</Label.GestureRecognizers>
</Label>
<Label x:Name="view4" Text="View 4" ZIndex="1" Margin="90,90,0,0" BackgroundColor="SkyBlue" Style="{StaticResource labelStyle}">
<Label.GestureRecognizers>
<TapGestureRecognizer Command="{Binding BringToFront}" CommandParameter="{Binding Source={x:Reference view4}}"/>
</Label.GestureRecognizers>
</Label>
</Grid>
Now, we are going to dynamically update the ZIndex value of the .NET MAUI views in the runtime. Here, we choose to bring the view to the front based on the click action. Refer to the following code example.
private async void OnBringToFrontAsync(object view)
{
var viewName = (view as Label).Text;
bool answer = await Application.Current.MainPage.DisplayAlert("Bring to front", "I am "+viewName + " , " + "Shall i move to front ?", "Yes", "No");
if (answer)
{
(view as Label).ZIndex = Zindex;
Zindex += 1;
}
}
 Resource
Resource
To play with ZIndex, you can use the dynamically update ZIndex in .NET MAUI project on GitHub.
Conclusion
I hope you now have a clear idea about using ZIndex in .NET MAUI applications.
The Syncfusion .NET MAUI suite offers more than 10 UI controls and libraries to build .NET MAUI applications. Try them out and share your feedback with us.
If you’re waiting a little longer before dipping your toes into MAUI, Syncfusion’s Xamarin suite offers over 150 UI controls, from basic editors to powerful, advanced controls like DataGrid, Charts, ListView, and Rich Text Editor.
If you have any comments or questions, you can contact us through our support forum, support tickets, or feedback portal. We are always happy to assist you!
Thanks for reading!